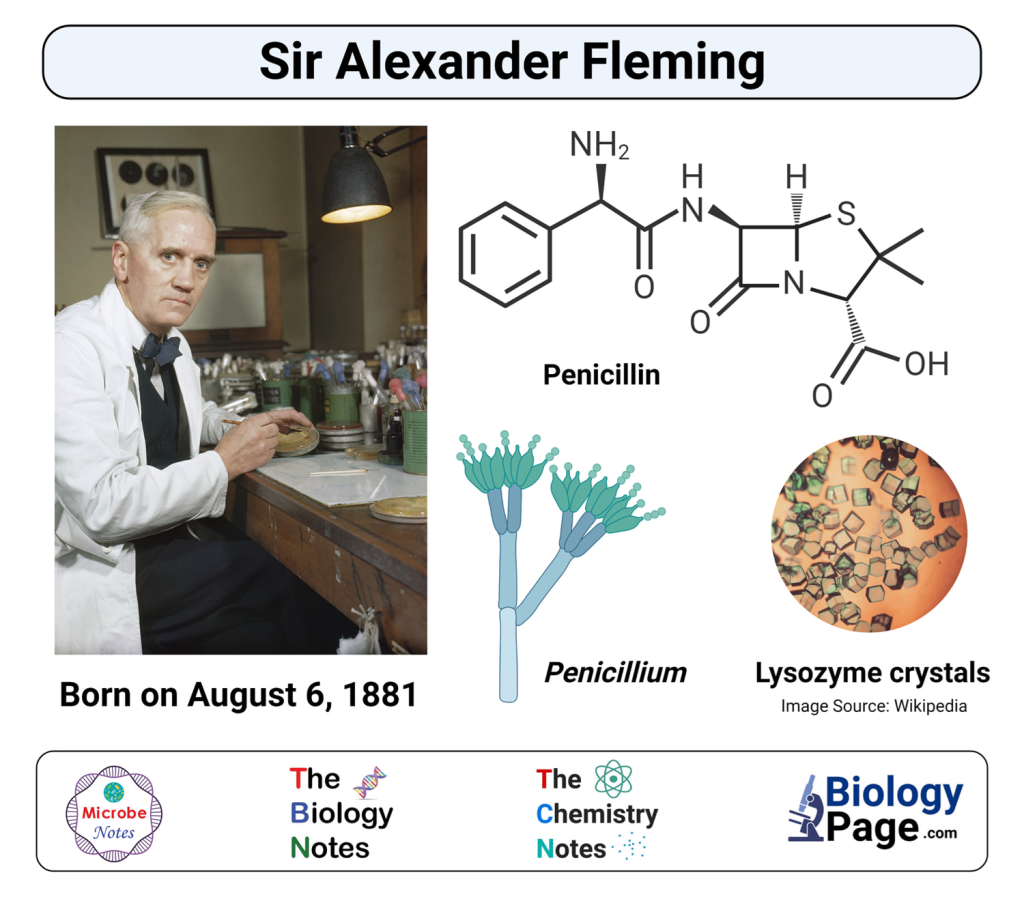
Alexander Fleming, a celebrated Scottish biologist, is renowned for his pioneering contributions in the field of microbiology. His remarkable discovery of penicillin’s antibiotic properties revolutionised medical practices and had a profound impact on human health.
Despite encountering criticism and scepticism from the scientific community, Alexander Fleming’s ground-breaking discovery of penicillin’s antibiotic properties revolutionized medicine. Initially met with limited enthusiasm, the potential of his discovery went largely unrecognized for several years. Moreover, the challenge of producing penicillin in large quantities hindered its widespread use. These setbacks shed light on the difficulties involved in translating scientific breakthroughs into practical applications.
Nevertheless, the impact of Fleming’s discovery cannot be overstated. Penicillin transformed the field of medicine by providing an effective treatment for bacterial infections, saving countless lives. Its success paved the way for the development of a wide range of antibiotics. Fleming’s significant contributions earned him prestigious accolades, including the shared Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Florey and Chain.
Born on August 6, 1881, in Lochfield, Scotland, Alexander Fleming developed a deep fascination with nature and a strong interest in biology during his upbringing in a rural farming community. After completing his early education, he pursued studies in biology, physiology, and pharmacology at the Royal Polytechnic Institution in London. This educational background laid the groundwork for his future scientific pursuits.
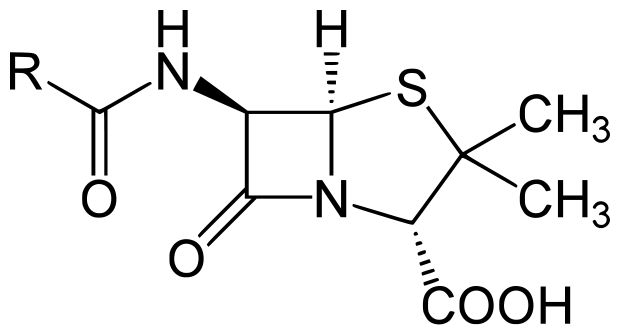
Working at St. Mary’s Hospital Medical School in London in 1928, Fleming stumbled upon a serendipitous discovery that would revolutionize medicine. His observation that the mould Penicillium notatum inhibited bacterial growth in a petri dish marked the birth of penicillin, the world’s first antibiotic. Through subsequent experiments and research, Fleming demonstrated the effectiveness of penicillin in treating bacterial infections, ushering in a new era in medical treatment.
Despite the immense potential of his discovery, Fleming faced significant challenges in the practical application of penicillin. One of the primary obstacles was the production of penicillin in sufficient quantities for therapeutic purposes. Initially, Fleming’s attempts to scale up production were met with limited success due to the difficulty of isolating and purifying the antibiotic. Overcoming this setback necessitated collaboration and further research with scientists like Howard Florey and Ernst Chain, who played pivotal roles in the development and mass production of penicillin.
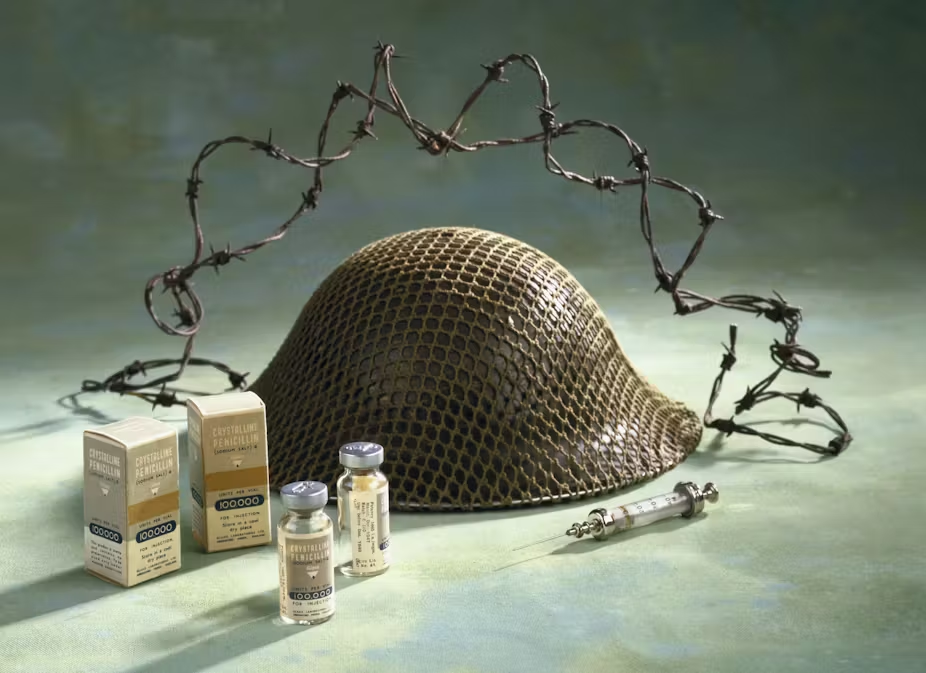

Alexander Fleming’s life and scientific journey provide valuable lessons for aspiring scientists and researchers. His ability to maintain curiosity, persistence, and openness to unexpected discoveries played a vital role in his success. Fleming’s work underscores the significance of collaboration and interdisciplinary approaches in advancing scientific knowledge. Furthermore, his failures serve as a reminder that setbacks and criticism are inherent parts of the scientific process, emphasizing the importance of perseverance in overcoming challenges.
In conclusion, Alexander Fleming’s remarkable contributions to microbiology, particularly his discovery of penicillin, revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections and laid the foundation for the development of antibiotics. Despite facing criticism and encountering obstacles in the production and recognition of penicillin’s potential, Fleming’s perseverance and ground-breaking work left an indelible impact on medicine and human health.